
Nuclear imaging uses radioactive tracers as a diagnostic tool to study the organs, tissues and other structures of the body. It's an alternative to other imaging methods such as X rays and CT scanners.
What is nuclear imaging?
Nuclear medicine imaging is a specialty of radiology that uses very small amounts of radioactive chemicals (radiopharmaceuticals) to study the function of your body. This is usually done to detect abnormalities very early in the course of a disease.
What are the risks?
The two biggest risks from nuclear imaging are radiation and allergic reactions. These are very rare, and most patients have no problem with these tests.
What are radioactive tracers?
Nuclear medicine uses many types of tracers. Some tracers have a very narrow application to a certain type of tissue or an organ. Some work on a broader basis, for example the ability of tracking blood in the body.
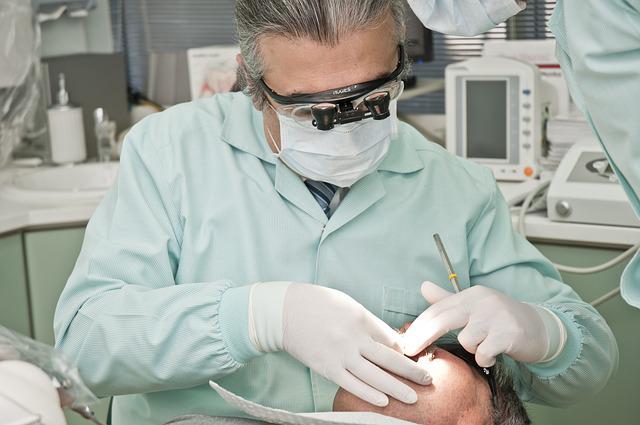
What do these radioactive tracers look like?
Tracers are made up of a series of carrier molecules that are bonded tightly to a radioactive atom. These molecules are usually placed either on the internal organs to be scanned or injected into a patient. Some tracers contain a special molecule, which interacts directly with the protein or sugar within the body.
What are different nuclear imaging techniques?
The most common nuclear imaging techniques are single-photon emission computedtomography (SPECT), as well as positron emission Tomography (PET). The two procedures produce images in three dimensions of the organs using radiopharmaceuticals.
SPECT utilizes gamma rays, which are emitted by radioactive tracers as they pass through the body. Gamma cameras produce digital signals from the gamma-rays. Computers use these signals to produce 3D images of internal organs.
How long does the nuclear scan last?
A nuclear scanning takes 30-60 minutes in addition to the time it takes for the patient to wait once the radioactive substance is administered. It can be done in a single visit or it can be spread over several days.
What are the most commonly scanned areas on your body?
The nuclear scan is performed on a rotating table. A camera on the SPECT captures images of your organs and body parts. These images are sent by computer to create 3D models of organs and body parts.
What are the different types of radioactive tracers that can used in nuclear imaging?
Doctors may use different radioactive tracer depending on the part of your body that is being scanned. These include various forms of the element technetium.
What do radioactive traces appear like?
Most radioactive traces are created by very specific molecules. These molecules can consist of a carrier-molecule that's tightly bound with a radioactive atomic tracer or a compound made up of special atoms that interact with proteins or sugars inside your own body.
FAQ
What would happen if Medicare was not available?
Uninsured Americans will increase. Some employers will drop their employees from their plans. Many seniors will also have higher out-of pocket costs for prescription drugs or other medical services.
What is an infectious disease?
Infectious disease can be caused by germs (bacteria or viruses) Infectious illnesses spread quickly via close contact. Measles, rubella (German measles), pertussis (whooping cold), rubella (German measles), measles), chickenpox and strep throat are just a few examples.
What do you think about the private sector's role?
The private sector has a vital role to play in delivering healthcare. It also provides equipment used in hospitals.
Some hospital staff are also covered by the program. It is logical for them to be involved in running the system.
However, there are limitations to what they can offer.
It is impossible for private providers to be competitive with services provided by the government.
They shouldn't attempt to manage the entire system. This could lead to a system that doesn't provide good value for money.
Statistics
- Consuming over 10 percent of [3] (en.wikipedia.org)
- For instance, Chinese hospital charges tend toward 50% for drugs, another major percentage for equipment, and a small percentage for healthcare professional fees. (en.wikipedia.org)
- Foreign investment in hospitals—up to 70% ownership- has been encouraged as an incentive for privatization. (en.wikipedia.org)
- Healthcare Occupations PRINTER-FRIENDLY Employment in healthcare occupations is projected to grow 16 percent from 2020 to 2030, much faster than the average for all occupations, adding about 2.6 million new jobs. (bls.gov)
- For the most part, that's true—over 80 percent of patients are over the age of 65. (rasmussen.edu)
External Links
How To
What is the Healthcare Industry Value Chain (or Value Chain)?
The healthcare industry value chain consists of all the activities involved in providing healthcare services to patients. This includes the operations of hospitals and clinics as a whole, and the supply chain that connects them to other providers. The end result is a continuum, which begins with diagnosis and ends at discharge.
The value chain is made up of four major components:
-
Business processes - These are the tasks performed throughout the whole process of providing health care. A physician might order medication for a patient, then perform an examination. Each step must be done correctly and efficiently.
-
Supply Chains - All the organizations involved in making sure that the right supplies reach the right people at the right time. One hospital may have many suppliers. This includes pharmacies and lab testing facilities as well as imaging centers and janitorial staff.
-
Networked Organizations - To coordinate these various entities, there must be some form of communication between the different parts of the system. Most hospitals have multiple departments. Each department has its own office and phone number. Each department will have its own central point, where employees can get updates and ensure everyone is informed.
-
Information Technology Systems - IT plays a critical role in business process efficiency. Without IT, things could quickly go sour. IT provides an opportunity to integrate new technologies into the system. Doctors can connect to a secure network connection in order to integrate electronic medical records into their workflow.